Saccharomyces boulardii is a probiotic of the class Saccharomyces that in certain situations can promote improvement. With possible properties and benefits for humans, it has certain recommendations.
Content
What is Saccharomyces boulardii and what is it for
It is a living bacterium considered a probiotic for its benefits for the intestinal flora. Taking Saccharomyces boulardii increases the gut microbiota, providing beneficial properties for humans.
Since the discovery of the boulardii strain, it has been tested in various studies and medical trials with people with intestinal and digestive problems, demonstrating its effectiveness in the treatment of candidiasis, caused by the yeast called Candida albicans, as well as for various disorders related to the large and small intestines.
In addition, the efficacy and results of using Saccharomyces boulardii have been demonstrated in people with poor intestinal flora, improving its reproduction and confirming the increase of microorganisms residing in the human digestive tract.
The tropical yeast strain called S. boulardii can be found in various foods and fermented products listed below.
Possible uses for candida and candidiasis
Being resistant to the use of antibiotics, Saccharomyces boulardii works in candidiasis, an infection caused by the pathogen Candida albicans that affects a considerable number of people, causing gastrointestinal discomfort, diarrhea, and other digestive tract disorders.
Against candida, it can be administered four hours after using antibiotics such as fluconazole to eliminate the infection, supporting the effects of the medications and maintaining a considerable number of microorganisms that will reinforce the intestinal flora.
The effects of boulardii are antisecretory, reducing the formation of toxins in the intestine and preventing the atrophy of intestinal villi (trophic effect).
It also works against other pathogenic microorganisms such as Escherichia coli, E. histolytica, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella typhi, and Shigella species, although generally the most common uses are against candida and the improvement of human microbiota.
Recommended at times to treat diarrhea
It is proving effective against various gastrointestinal disorders, having uses for diarrhea.
Continuous research with patients and people suffering from temporary or chronic loose stools shows that taking a daily dose of Saccharomyces boulardii for diarrhea has the following benefits:
- Prevent diarrhea after taking antibiotics in adults, children, and the elderly.
- Avoid digestive problems in patients with nasogastric tube feeding.
- Reduce cases of acute diarrhea in children and babies. Results are visible from 1.5 days.
- Reduce other cases of loose stools and poor stool control in other cases of diarrhea in babies, making the disorder last less time and recovery better.
- Retroviral diarrhea: acts by controlling and reducing cases.
- Against gastrointestinal discomfort and diarrhea caused by the bacterium Clostridium difficile, both in people who already have it and acting as an element to prevent it when it is diagnosed that it is present in the individual's body. In many cases, boulardii is administered to avoid the side effects of antibiotics, avoiding the reduction of intestinal flora.
- HIV diarrhea acts in the same way, that is, shortening the times it is present, as well as avoiding some cases.
- As an aid to prevent traveler's diarrhea, caused by the change in water that is ingested, as well as by contact with other microorganisms to which the human body is not accustomed.
With Helicobacter pylori in some cases
Against this gram-negative spiral-shaped bacterium, it is also widely used. Saccharomyces boulardii for Helicobacter pylori has the following benefits:
- Control of the proliferation of pathogens, growth, and development by competing for prebiotic foods and habitable space in the intestine.
- Reduction of abdominal pain and the side effects of H. pylori bacteria.
The use of S. boulardii is always done in conjunction with medications to reduce adverse reactions to treatment, as well as to control symptoms after eradicating Helicobacter pylori, having no benefits as a probiotic that eliminates the pathogen but instead acting as a complementary therapy to reduce the discomfort caused by the infection and the possible side effects of antibiotics.
Acne
In cases where acne appears due to a hormonal imbalance, it seems to have beneficial effects. It should be taken along with a healthy and balanced diet to combat the formation of pimples and blackheads, as well as foods rich in omega-3.
Saccharomyces boulardii for acne can facilitate the reduction of papules and pimples when used with a specific treatment, administering boulardii in doses of 100 mg and 250 mg according to the severity of the acne.
Its benefits are complementary to anti-acne treatment, and satisfactory results cannot be found when only taking the probiotic. Although S. boulardii is effective against acne, improving appearance and reducing inflammation, it is always appropriate to use it with the recommendation of a specialist in hormonal disorders.
Sometimes works with Blastocystis hominis
In the fight against intestinal parasites, it has some effectiveness. Saccharomyces boulardii for Blastocystis hominis can reduce the diarrhea caused by this microorganism and reduce its presence when stool studies are conducted.
Studies have been conducted where antibiotics and S. boulardii were administered to verify the efficacy of both treatments, resulting in a decrease in both groups of patients.
One group was given metronidazole and the other the probiotic Saccharomyces boulardii for more than 2 weeks, resulting in a reduction in the number of pathogenic microorganisms in the stool in both cases.
However, it is not recommended to take only probiotics to control B. hominis infection. For greater efficacy and better control, both treatments should be administered as with other bacterial and fungal infections.
Sometimes can help with eczema
In some cases of skin tissue inflammation, it can be beneficial by stimulating the immune system and regulating its autoimmune response or against inflammation caused by contact with substances and chemicals.
Saccharomyces boulardii for eczema can regulate the intestinal flora, improving the inflammatory symptoms of the skin.
Although it seems that the health of the intestine is unrelated to the skin tissue, studies have indicated that good quality human microbiota reduces the discomfort of eczema as well as many skin pathologies.
It is usually recommended to take S. boulardii with lactobacilli and bifidobacteria to increase its effectiveness.
Use against Clostridium difficile
Clostridium difficile is a gram-positive bacterium that causes diarrhea in humans, both in children and adults. This type of bacillus is part of the intestinal microbiota, not producing side effects when the colony size is small.
However, when it increases and its size becomes considerable, it can produce discomfort and disorders that are advisable to treat.
To control and eradicate Clostridium difficile, Saccharomyces boulardii and metronidazole are used.
This bacterium, which initially is not pathogenic, when it increases uncontrollably due to a reduction of the normal intestinal flora, causes diarrhea.
To avoid the discomfort it produces, S. boulardii has been tested with considerable efficacy, both in shortening its duration and in preventing it in hospitalized patients and those on antibiotic treatment.
Taking it, in addition to reducing the occurrence of new episodes of loose stools, also works as an adjuvant or complementary therapy to avoid the side effects of medications administered to reduce the bacterial colony of C. difficile causing the diarrhea.
Possible benefits as a probiotic
As a probiotic, it is widely used as it facilitates the repopulation and growth of intestinal flora. By including it in the diet with foods or through capsules of Saccharomyces boulardii 250 mg, 200 mg, or 100 mg, one can perceive the increase of beneficial live bacteria for health, preventing other pathogens from colonizing the intestine.
Saccharomyces boulardii probiotic helps us maintain a healthy, strong, and large bacterial colony, providing relief for heavy digestions, intestinal gases, and better utilization of nutrients from food. It also speeds up food decomposition, making it spend less time in the digestive tract and ferment in less time, reducing the appearance of CO2 in the intestine and many cases of flatulence.
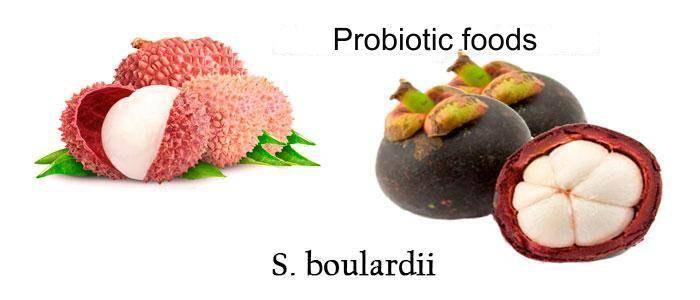
Foods Containing Saccharomyces
Saccharomyces boulardii is present in probiotic foods such as mangosteen and lychee, foods from which it was first isolated in 1923 by the French scientist Henri Boulard.
Probiotics Related to Saccharomyces
As it belongs to the Saccharomyces spp class, boulardii has similar benefits and shares many characteristics with Saccharomyces cerevisiae, sharing taxonomic parcels and properties for humans.
However, this probiotic strain is different from cerevisiae, considered the beer probiotic.
As we have explained in this article, boulardii is effective against diarrhea and gastrointestinal problems, also with some efficacy in Irritable Bowel Syndrome, Colitis, and other conditions of the small and large intestines.
Other Related Lactobacilli
References
- Malgoire JY, Bertout S, Renaud F, Bastide JM, Mallié M (2005). «Typing of Saccharomyces cerevisiae clinical strains by using microsatellite sequence polymorphism». Clin. Microbiol. 43 (3): 1133-7.
- Remenova T, Morand O, Amato D, Chadha-Boreham H, Tsurutani S, Marquardt T. «A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial studying the effects of Saccharomyces boulardii on the gastrointestinal tolerability, safety, and pharmacokinetics of miglustat». Orphanet J Rare Dis 2015;10:81.
- McFarland L, Bernasconi P (1993). «Saccharomyces boulardii: a review of an innovative biotherapeutic agent». Microb Ecol Health.
- Riaz M, Alam S, Malik A, Ali SM. «Efficacy and safety of Saccharomyces boulardii in acute childhood diarrhea: a double blind randomised controlled trial». Indian J Pediatr 2012.
- Romanio MR, Coraine LA, Maielo VP, Abramczyc ML, Souza RL, Oliveira NF. «Saccharomyces cerevisiae fungemia in a pediatric patient after treatment with probiotics». Rev Paul Pediatr 2017.
- Goldenberg JZ, Ma SS, Saxton JD, et al. «Probiotics for the prevention of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea in adults and children». Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013.
- Lau CS, Chamberlain RS. «Probiotics are effective at preventing Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea: a systematic review and meta-analysis». Int J Gen Med.
- Pozzoni P, Riva A, Bellatorre AG, et al. «Saccharomyces boulardii for the prevention of antibiotic-associated diarrhea in adult hospitalized patients: a single-center, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial». Am J Gastroenterol 2012.
- Suganthi V, Das AG, J Clin Diagn «Role of Saccharomyces boulardii in reduction of neonatal hyperbilirubinemia».
- Roy U, Jessani LG, Rudramurthy SM, et al. «Seven cases of Saccharomyces fungaemia related to use of probiotics». Mycoses 2017.